The Future of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
The Future of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
In the Arena of Scientific Education, education is an important detail in the preparation of other technology of healthcare professionals. Historically, clinical students and specialists trusted textbooks, corpses and conventional methods of learning anatomy, methods and affected care for a person. However, with rapid progress in technology, especially virtual reality (VR), the medical school undergoes a significant transformation.
The virtual fact gives a absorbing, interactive and quite practical environment that allows medical participants to simulate complex tactics, understand human anatomy in 3-D and even interact with digital suffering in real time. This generation is ready to trade with a medical education panorama through a range of more useful, more efficient and safer study opportunities for scientific experts. In this newsletter, we are exploring the function of digital truth in clinical education, his blessing, demanding situations and fatal opportunities that lie ahead of us.
What is Virtual Reality in Medical Training?
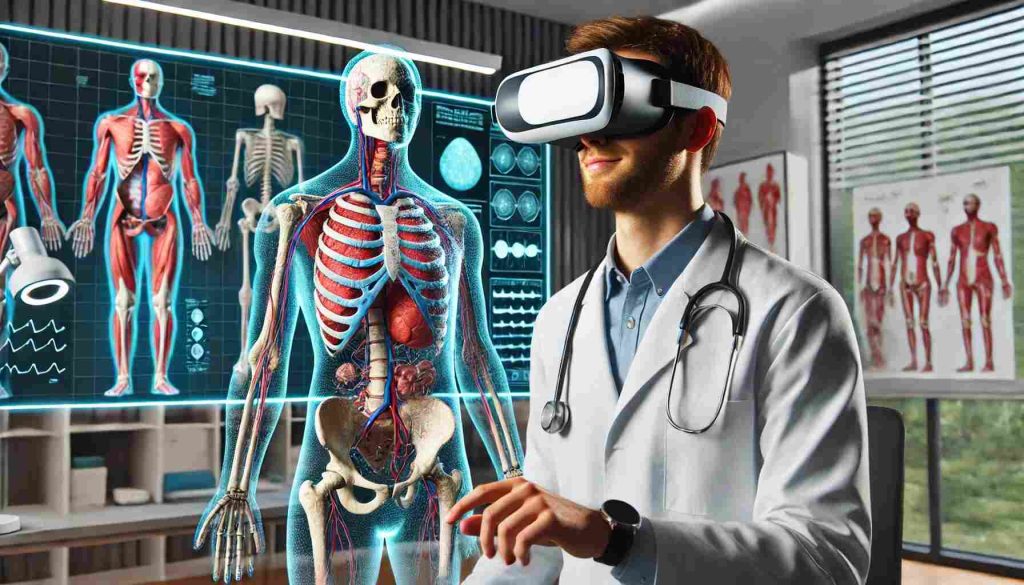
Virtual reality in clinical training concerns the use of computer -generated simulations to duplicate real international scientific situations. VR Generation enables university students, documents and health specialists to immerse themselves in simulated environments that intentionally resemble real situations. These simulations can be diverse from simple anatomy training to extremely complicated surgery and emergency clinical approaches.
VR Gear in medical education usually includes headsets, haptic notes and movement controllers, all of which allow the person to have an interaction with digital international. With the help of VR, clinical participants can interact in PALMS-ON exercise without risks related to traditional techniques such as practicing patients or running with corpses.
The Benefits of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
Immersive Learning Experience: One of the most significant advantages of VR is its ability to create highly immersive experiences. Unlike traditional 2D learning tools such as books or videos, VR allows users to “step into” the simulated environment and interact with it. This hands-on experience can significantly improve retention and understanding of complex concepts.
For example, medical students can use VR to explore 3D models of the human body, including organs, tissues, and systems. This level of immersion helps them better understand anatomy and physiological processes in a way that is not possible with textbooks or traditional learning methods.
Safe Simulation of High-Risk Procedures: Virtual reality offers a safe environment where medical professionals can practice high-risk procedures without the fear of making mistakes that could harm a patient. Surgeons, for example, can perform virtual surgeries and practice complex techniques in a controlled setting. VR simulations allow them to gain valuable experience and build muscle memory, preparing them for real-life scenarios.
Additionally, VR can simulate emergency medical situations, such as trauma care or CPR, allowing healthcare providers to practice life-saving techniques repeatedly until they achieve proficiency.
Cost-Effective Training: Medical education is often expensive, with the costs of cadavers, medical equipment, and real-time patient simulations adding up quickly. VR offers a more affordable solution, as it eliminates the need for physical resources and provides scalable training options. Instead of relying on cadavers, which may be limited in number and availability, VR can simulate various anatomy and conditions, offering limitless training possibilities.
Moreover, VR can be used across multiple learning stages, from basic anatomy lessons to advanced surgical training, reducing the overall cost of training while maintaining high-quality education.
Remote Learning and Accessibility: Another advantage of VR is the ability to bring medical training to locations where access to traditional medical education might be limited. Healthcare professionals in rural or underserved areas can access virtual reality training programs from the comfort of their homes or local clinics, ensuring that quality education is available to all, regardless of geographical constraints.
Remote VR training programs also allow medical students and professionals to practice on-demand, at their own pace, and according to their own schedules, offering flexibility in their learning process.
Improved Patient Care: By allowing medical professionals to refine their skills and gain hands-on experience in a virtual setting, VR can ultimately lead to better patient care. Doctors and surgeons who have undergone VR training are more likely to perform procedures with greater accuracy and confidence. As a result, patients benefit from improved outcomes and a reduced risk of errors during medical interventions.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
Surgical Training: One of the most exciting applications of VR in medical training is in the field of surgery. VR allows surgical trainees to practice and refine their skills in a realistic virtual environment. Surgeons can simulate complex operations, such as brain surgery or heart surgery, allowing them to practice the procedures multiple times before performing them on a real patient.
These VR simulations provide immediate feedback, helping trainees assess their performance and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, advanced VR tools are equipped with haptic feedback, which simulates the sensation of touch, providing a more authentic training experience.
Medical Simulations and Diagnostics: In addition to surgical training, VR is used to train medical professionals in diagnostics, such as interpreting medical imaging (e.g., X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans). Medical trainees can use VR to view 3D representations of images and practice diagnosing conditions like tumors, fractures, or abnormalities in a more interactive and engaging way.
Virtual reality also enables simulations of different medical scenarios, such as diagnosing and treating rare diseases. This is invaluable in improving diagnostic skills and ensuring that healthcare professionals are well-prepared to handle various medical conditions.
Anatomy Education: Virtual reality is revolutionizing the way medical students learn human anatomy. Traditional methods, such as studying 2D images or dissecting cadavers, have limitations in terms of interactivity and scalability. VR allows students to explore and interact with 3D models of the human body, providing a deeper understanding of anatomical structures and their functions.
These 3D models can be manipulated to view organs, muscles, bones, and blood vessels from different angles and in various states, providing a more comprehensive understanding of human anatomy than traditional methods.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: VR is also being used to aid in the rehabilitation of patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. VR-based physical therapy programs can help patients perform exercises in a virtual environment, providing real-time feedback and progress tracking. These programs are often engaging, helping to motivate patients during their recovery process.
Additionally, VR allows therapists to monitor a patient’s progress remotely and adjust their treatment plan as needed. This can be especially beneficial in telemedicine and remote rehabilitation settings.
Challenges and Limitations
While virtual reality holds immense potential, there are still challenges to overcome before it becomes widely integrated into medical training. These include:
- High Initial Costs: Although VR offers cost-effective training in the long run, the initial investment in VR hardware, software, and training modules can be expensive.
- Technology Barriers: VR systems require specialized equipment, such as headsets and controllers, which may not be accessible to all institutions or individuals.
- Technical Limitations: While VR technology has come a long way, there are still limitations in terms of realism, particularly in simulating complex human interactions or emotional responses from virtual patients.
The Future of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
The future of virtual reality in medical training looks incredibly promising. With continuous advancements in VR technology, medical education is set to become more immersive, personalized, and accessible. As VR hardware becomes more affordable and user-friendly, it will be integrated into everyday medical training programs, from medical schools to hospitals and clinics.
In the years to come, VR is expected to play an even larger role in medical research, helping to simulate and study complex medical conditions or surgical techniques that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to explore in real life. Additionally, VR will continue to evolve alongside AI and machine learning technologies, creating even more intelligent and adaptive training environments.
Conclusion
Virtual reality is undoubtedly transforming medical training, offering unprecedented opportunities for students, doctors, and healthcare professionals to learn, practice, and improve their skills in a safe, cost-effective, and engaging environment. As VR technology continues to evolve, its potential to revolutionize medical education and improve patient care is limitless. The future of VR in medical training is not just a trend; it is a pivotal development in shaping the future of healthcare education.